 |
|
|||||||||
| Home | History | Support | Articles | Screenshots | Download | F.A.Q. | Beta Area | Advertise here |
|
SpeedFan 4.52 Copyright 2000-2020 by Alfredo Milani Comparetti |
SpeedFan 4.44 introduced a new and improved fan control strategy. Let us first recall some concepts and
definitions:
- any computer can have any number of fans, from 0 up.
- On a specific computer, SpeedFan might be able to read fan speed RPMs (Revolutions Per Minute). SpeedFan might not be able to read the RPMs of all installed fans. If SpeedFan can read no RPM, check for future SpeedFan releases as hardware support improves over time.
- On a specific computer, SpeedFan might be able to access SPEED controls (usually referred to as PWMs). If you would like to know more about PWM, feel free to read this article. Please note that RPM readings and PWM settings are not necessarily tied together. The hardware monitor chips located inside computers have some wires to read fan speeds and some others to control PWMs. It is up to the computer manufacturer to decide whether and how to connect those wires. Understanding which SPEED (PWM) acts (controls) which fan can be a matter of trial and error, but it is worth the effort.
- Every fan reacts to PWM control differently. 4-wire fans usually exhibit a rather linear response. 3-wire fans can be much less linear. It depends on several factors, including the circuitry on the motherboard and the type of fan used.
 That said, let's move on and have a look at the basic concepts behind SpeedFan's Advanced Fan
Controllers. A Fan Controller links a specific PWM control (the Controlled Speed) to the current
value of any number of source temperatures. For each temperature we can define the response curve.
This means that we can define what PWM value we want to apply for every temperature value. Each
temperature can have a different response. Let's see how to create our own first Fan Controller.
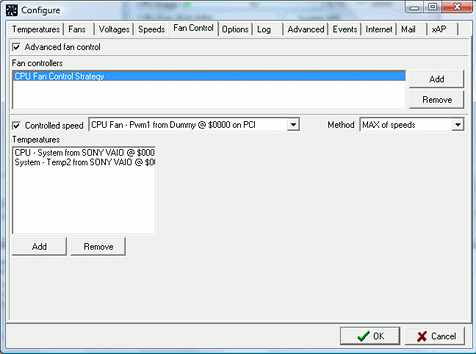
Start SpeedFan, press CONFIGURE button and select the Fan Control tab. Enlarge the window if
needed. In the example image we have already created a Fan Controller and called it "CPU Fan
Control Strategy". We can create more using the Add button on the right. With the Remove button
we can delete a fan controller we previously created. As soon as we select "CPU Fan Control
Strategy" in the list box, its parameters will appear below in the window. A Fan Controller
requires a PWM to act on. Multiple temperatures can be used to control the PWM. For each
temperature is defined its response curve. The final value applied to the controlled PWM
depends on the selected method: either MAX of speeds or SUM of speeds. When a
temperature is selected in the list box, the relevant configuration parameters appear on the
left side.
That said, let's move on and have a look at the basic concepts behind SpeedFan's Advanced Fan
Controllers. A Fan Controller links a specific PWM control (the Controlled Speed) to the current
value of any number of source temperatures. For each temperature we can define the response curve.
This means that we can define what PWM value we want to apply for every temperature value. Each
temperature can have a different response. Let's see how to create our own first Fan Controller.
Start SpeedFan, press CONFIGURE button and select the Fan Control tab. Enlarge the window if
needed. In the example image we have already created a Fan Controller and called it "CPU Fan
Control Strategy". We can create more using the Add button on the right. With the Remove button
we can delete a fan controller we previously created. As soon as we select "CPU Fan Control
Strategy" in the list box, its parameters will appear below in the window. A Fan Controller
requires a PWM to act on. Multiple temperatures can be used to control the PWM. For each
temperature is defined its response curve. The final value applied to the controlled PWM
depends on the selected method: either MAX of speeds or SUM of speeds. When a
temperature is selected in the list box, the relevant configuration parameters appear on the
left side.
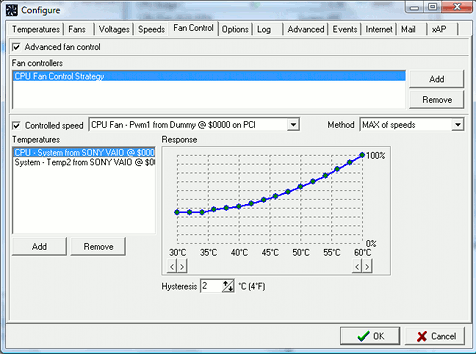 The response curve determines the requested PWM value (ranging from 0% to 100%) depending on
the current temperature. By using the "<" and ">" buttons, the minimum and the maximum
temperature levels can be selected. If the current temperature is below the minimum, the
selected PWM value will be the one assigned to the minimum temperature. If the current
temperature is higher than the maximum, the selected PWM value will be the one assigned
to the maximum temperature. The hysteresis value is used to avoid fan fluctuations.
In a few words, when the temperature rises, the new PWM value is applied immediately. When
it lowers, the last applied PWM value is kept until the current temperature is hysteresis
degrees lower than the temperature that caused the current PWM to be applied.
The response curve determines the requested PWM value (ranging from 0% to 100%) depending on
the current temperature. By using the "<" and ">" buttons, the minimum and the maximum
temperature levels can be selected. If the current temperature is below the minimum, the
selected PWM value will be the one assigned to the minimum temperature. If the current
temperature is higher than the maximum, the selected PWM value will be the one assigned
to the maximum temperature. The hysteresis value is used to avoid fan fluctuations.
In a few words, when the temperature rises, the new PWM value is applied immediately. When
it lowers, the last applied PWM value is kept until the current temperature is hysteresis
degrees lower than the temperature that caused the current PWM to be applied.
Additional relevant configuration settings
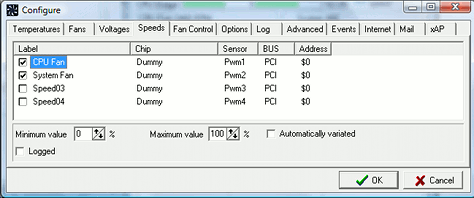 The SPEEDS tab allows to set some parameters for each PWM control. The Advanced Fan Control
strategy keeps into consideration the "Minimum value" and the "Maximum value" set in this
tab. This means that if the computations based on the temperature response curves lead to,
say, a PWM value of 30%, but the SPEEDS tab defines 45% as the minimum value for that PWM,
45% will be used instead. These settings are shared with the standard fan control method.
The SPEEDS tab allows to set some parameters for each PWM control. The Advanced Fan Control
strategy keeps into consideration the "Minimum value" and the "Maximum value" set in this
tab. This means that if the computations based on the temperature response curves lead to,
say, a PWM value of 30%, but the SPEEDS tab defines 45% as the minimum value for that PWM,
45% will be used instead. These settings are shared with the standard fan control method.
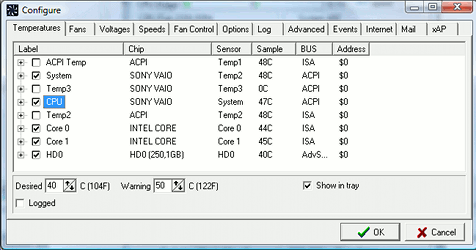 The TEMPERATURES tab allows to define a warning level for each temperature. This warning
level is taken into consideration by the Advanced Fan Control strategy: if a
temperature exceeds its warning level, SpeedFan will forcibly set the relevant PWM to 100%.
The TEMPERATURES tab allows to define a warning level for each temperature. This warning
level is taken into consideration by the Advanced Fan Control strategy: if a
temperature exceeds its warning level, SpeedFan will forcibly set the relevant PWM to 100%.
Activating the Automatic Fan Speed checkbox on the main screen enables fan control.
Whether the old fan control or the new Advanced Fan Control strategy is used depends on the
Advanced Fan Control checkbox on the FAN CONTROL tab of the CONFIGURE window. If it
is not set, the old fan control style is used.
Work in progress
This feature is a long awaited one. I speeded up development and release to the public. Suggestions
are welcome.
|
You can rate this article.
|
By Alfredo Milani Comparetti (alfredo [at] almico.com)
|
| Page generated in 0.0846 seconds | Powered by (new)... | Page viewed 2429510 times |
| - | Did you know that SpeedFan has an |
Privacy policy |